What's covered
- Understand the difference between the technology used for backup and the technology used for replication that enables disaster recovery
Original article: https://www.zerto.com/resources/a-to-zerto/the-differences-between-backup-and-replication/
Read Article
The terms backup and replication are often (and inaccurately) used interchangeably. There are advantages and disadvantages to both, and knowing the difference between these two technologies is critical for picking the solution that is right for your business.
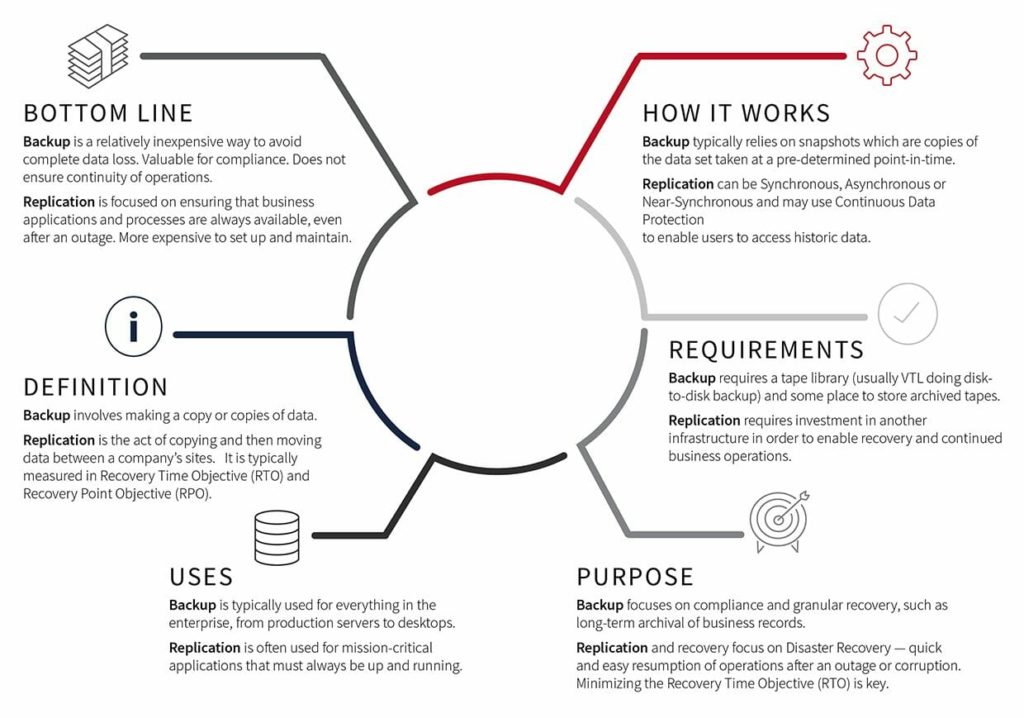
Backup involves making a copy or copies of data and storing them offsite in case the original is lost or damaged.
Replication is the act of copying data and then moving data between a company’s sites, whether those be datacenters, colocation facilities, public, or private clouds.
Choosing the technology that is best suited for your business can be challenging. Fortunately, we have summarized the main differences between backup and replication to explain some of the key distinctions:
4 Reasons Why Backup is Not Replication
Service Levels
Backups typically occur once per day and at night, which means that the potential data loss could be days or more. When protecting the applications and data that matter to your business, this amount of data loss is unacceptable. Restoring from a backup, especially a tape backup, can take days; from disk it might be slightly faster – a few hours
Application Impact
Backups rely on snapshot-based technology. The reason they are taken so infrequently is because this type of technology drains resources on the server. It is possible to take more frequent copies, but this comes at the expense of server resources and-user productivity is significantly impacted
Reverse Protection
Once applications and data have been made available at a target site, protection must be extended to include the new data that users are creating. A backup solution will not start taking backups and ship them back to the production site. Replication technologies will replicate back to the source site, ensuring the application is still protected both during and after an outage.
Retention
Backups are normally stored for a very long time for compliance and audit purposes. Depending on how often they occur, the recovery granularity can be hours, days, or more. Technologies that using Continuous Data Protection (CDP) offer extremely granular recovery points, often separated by mere seconds. This gives your enterprise several points in time to recover to, just in case the last point in time is corrupted.
Backups are relatively inexpensive ways to maintain some level of protection. However, today’s digital consumers demand an always-on level of service that backups simply cannot provide. The Zerto IT Resilience Platform™ is changing the way companies think about protecting their data, providing a single platform for all your data protection needs. If you’re interested in learning more, make sure to check out the DR 101 eBook to learn the fundamentals of replication, disaster recovery and IT Resilience.






